Students
Zhuang Wu
Summary
The objective of this project is to model the transport of contaminates in the primary loop of sodium cooled fast reactors. Sodium has been used for many year as a coolant for fast spectrum reactors and is proposed for some Gen IV reactor designs.
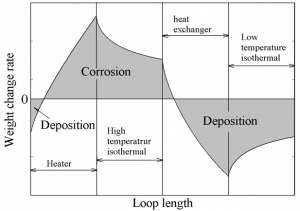
During operation, the sodium coolant begins to carry contaminates, which can be deposited in the primary loop. This deposition, which depends on the temperature profile of the coolant system, changes the properties of both the coolant and the inner surface of the structures, resulting in performance degradation and material failure.
- Apply the programming method to calculate the basic theoretical equation to determine it’s accuracy. The solution of the bulk concentration in a closed non-isothermal loop is:
\( c_{i,b}^′ (ξ)=∑_k \frac{b_k (1-2πki/l)}{1-4k^2 π^2/l^2} exp\left[\frac{2πkiϕ(ξ)}{l}\right]\)
- Try to extend basic equations by the principle of metal corrosion to apply in special corrosion situations. For multi-modular loop systems, the solution of the bulk concentration is:
\( c_b (ξ)=\frac{\bar{L}}{Q}∫_{ξ_0}^ξ F[x(s)]p[x(s)]q(s)ds+c_b (ξ_0) \)
In order to carry out this project, we will be using the Multiphysics Object Oriented Simulation Environment (MOOSE) to model the corrosion production, transport, and deposition in the reactor system. As a first estimate, a simplified model will be used to simulate the heat source, heat sink, and flow in the system. The purpose of using the simplified model is to make sure the week form of the equations have been developed correctly for the MOOSE framework. These scoping calculations will be done using two dimension models and simplified grid shown below.

Existing MOOSE mass, momentum, and energy equations will be used to model the heat source and transport of the corrosion particles in the flow.