Shoreline Mapping Software provides a modern, efficient alternative and complement to traditional coastline monitoring, reducing the need for labor-intensive field measurements. Undergraduate student Noah Evans, with the assistance of graduate student Stephen Adusei and Dr. Nina Stark, is using CoastSat to streamline the process of coastline mapping and adapting its process to address regional challenges. CoastSat is an open-source Python-based tool developed at UNSW Sydney, to extract and analyze shoreline dynamics using satellite imagery from Landsat and Sentinel satellites. Accessed through Jupyter Notebooks, CoastSat enables time-series analysis of coastlines by automating shoreline detection based on a user-defined reference baseline. Building off the user defined shoreline, CoastSat uses a combination of multi-spectral imaging, the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI), and machine learning-based classification to differentiate between sand, water, and other features with high precision. To further enhance accuracy, tidal correction techniques are applied using data from NOAA stations. This allows for a comprehensive assessment of coastal evolution, sea level rise, and impacts from storms and hurricanes. By streamlining the analysis process, CoastSat provides detailed insights into shoreline changes, supporting coastal management and predictive modeling efforts without the need for extensive field data collection.
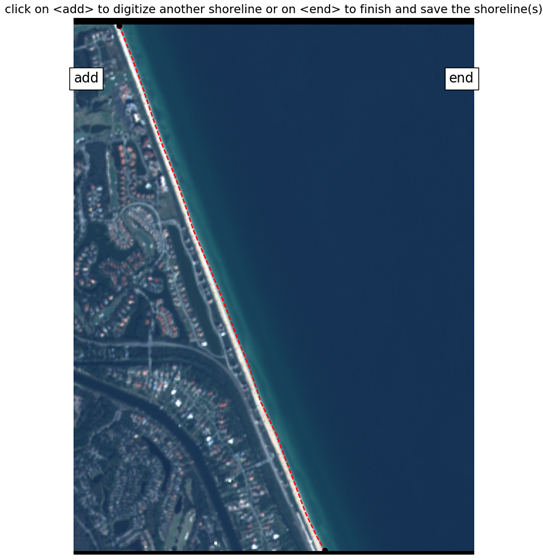
User Defined Reference Shoreline
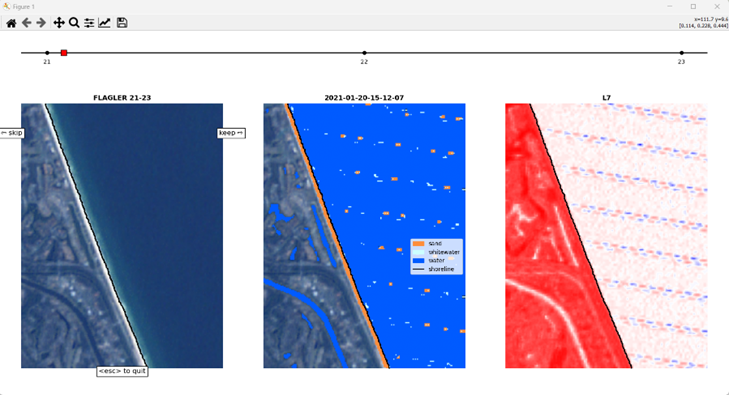
Batch Shoreline Detection
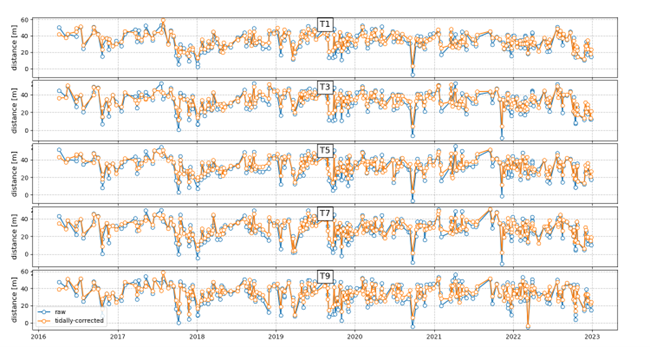
Tidally Corrected Shoreline Change